Optical Measurement and Statistical Analysis of Instantaneous Wall-Shear Stress in a Turbulent Boundary Layer
-
摘要: 采用近壁粒子图像测速(particle image velocimetry,PIV)技术实现了中低Reynolds数光滑平板湍流边界层瞬时摩擦阻力的测量.发展了单行互相关算法和迭代拟合技术估算瞬时摩擦阻力,其法向空间分辨率可达到2~4 pixel.作为对比,同时分析了相似Reynolds数范围的直接数值模拟数据.统计结果表明:摩擦阻力的脉动强度随Reynolds数升高呈现对数增长趋势,证实了外区大/超大尺度结构对壁面的影响.谱分析结果表明近壁区的低速条带结构主导着摩擦阻力的多尺度脉动特性,外区大/超大尺度结构对摩擦阻力的印迹作用较小,其主要通过调制作用实现对摩擦阻力的影响,这一结论可以从瞬时摩擦阻力的偏度以及概率密度函数曲线具有Reynolds数不变性得到进一步证实.Abstract: The near-wall PIV technique was utilized to measure the instantaneous wall-shear stress (WSS) in a smooth-wall turbulent boundary layer at low-to-moderate Reynolds numbers. The algorithm of single-row cross correlation, together with a newly proposed iterative fitting method, was used to estimate the WSS. The spatial resolution of WSS was about 2~4 pixel in the wall-normal direction. Existing direct numerical simulation datasets in the same Reτ range were also analyzed for direct comparison. The fluctuating intensity of WSS was found to follow the empirical log-law correlation with Reτ, indicating the existence of the influence of outer-layer large-scale or very-large-scale motions (LSMs/VLSMs) on the wall. A further spectra analysis indicates that the near wall low-speed streaks dominate the dynamic behavior of the WSS. Combined with weak Re-dependency of both the skewness and probability density function of fluctuating WSS, it can be inferred that the LSMs/VLSMs leave a mild footprint on the wall. Instead, the amplitude modulation effect is inferred to play a more prominent role in affecting the statistics and multi-scale characteristics of WSS.
-
0. 引言
摩擦阻力(以下简称摩阻, τw)是当流体与固壁面发生相对运动时, 由于流体的黏性, 在固体表面上产生的黏性阻力.航行器(比如汽车、飞机以及轮船等)中的摩阻在总阻力中占据很大比例, 例如, 对于亚声速运输机来说, 摩阻可以达到总阻力的50%[1].准确测量摩阻对于评估航行器的力学性能具有重要指导意义[2].此外, 摩阻的精确测量对于科学研究也非常重要:平均摩阻τw是壁湍流标度率中的一个关键物理量, 决定了平均摩擦速度uτ或黏性尺度l*[3-4], uτ=√ˉτw/ρ, l*=ν/uτ, ρ表示流体密度, ν表示流体运动黏性系数; 此外, Karman常数κ的取值一直以来都是一个有争议的话题[5], 目前认为此数值的取值在0.2~0.45之间, 对于高Reynolds数摩阻的准确测量有助于确定普适性更高的Karman常数.
截止到目前, 采用实验或者数值的方法能够实现平均摩阻的高精度测量, 其Reynolds数效应在学术界也取得了比较一致的认识.然而, 对于瞬时摩阻的测量以及多尺度脉动特性研究相对较少, 比如如何表征摩阻脉动强度στw的Reynolds数效应尚存争议.早期的观点认为采用平均摩阻无量纲的脉动强度是一个固定值, 不随Reynolds数变化, 即στw+=στw/τw=0.4, 对于湍流边界层(turbulent boundary layer, TBL)[6-10]以及槽道湍流(turbulent channel flow, TCF)[11-12]的研究结果均验证了这一观点, 具体可参考表 1所示前人研究结果总结.表中Reynolds数定义:Reδ=δU∞/ν,δ为边界层厚度,U∞为自由来流速度;Reh=hU∞/ν,h为槽道半宽度;Reθ=θU∞/ν,θ为动量损失厚度;Reτ=δuτ/ν.然而, 随着高精度定制传感器的使用, 近些年来对于低Reynolds数TCF的研究结果表明στw+值在0.2~0.45间浮动. Schlatter等[13]基于大量直接数值模拟(direct numerical simulation, DNS)数据发现在TBL中, στw+随着摩擦Reynolds数Reτ升高呈现缓慢增大的趋势, 其关系可用对数关系式表征: στw+=0.298+0.018lnReτ, 很多前人的DNS研究结果均证实了此对数标度率, 可参考表 1.此对数关系揭示了壁湍流对数区的大/超大尺度结构(large-scale motions or very-large-scale motions, LSMs/VLSMs)对摩阻的影响, 然而此标度率在高Reynolds数下是否仍然成立还须采用实验的方法进一步验证.对于摩阻的3阶统计矩(偏度, 记为Sτw), 目前学术界缺少统一认识, 表 1所示前人结果均表明Sτw≈1且呈现弱Reynolds数效应.在高Reynolds数下Sτw是否仍然满足此规律还需要进一步研究.
表 1 前人对于瞬时摩阻统计特性研究结果总结(标记在图 6中应用)Table 1. Summary of previous studies on the statistics of wall-shear stress (The symbols listed in the table are used in Fig. 6 for the related work)references flow types Re methods symbols στw+ Sτw Alfredsson et al[6] TBL
TCFReδ=28 000
Reh=3 800,5 000flush-mounted hot wire/hot film none 0.4 1 Österlund [14] TBL Reθ=2 500~9 800 hot wire 
0.36~0.4 not given Miyagi et al[11] TCF Reh=8 758~17 517 micro shear stress imaging chip none 0.4 1 Keirsbulck et al[15] TCF Reτ=74~400 electrochemical probe ■ 0.32~0.40 0.91~1.17 Mathis et al[16] TBL Reτ=4 480 hot wire 
0.4 1 Willert[17] TBL Reτ=240 PIV 
0.41 0.80 Li et al[18] TBL Reθ=1 009~4 070 μ-PTV 
0.39~0.43 not given Gubian et al[19] TCF Reτ=230~950 flush-mounted hot wire ○ 0.28~0.44 1.13~1.44 Liu et al[20] TCF Reτ=860, 1 300 MPS □ 0.28/0.29 0.88/1.3 Abe et al[21] TCF Reτ=180, 395, 640 DNS ◇ log-law not given Hu et al[22] TCF Reτ=90~1 440 DNS ▲ log-law 0.96~1.14 Schlatter et al[13] TBL Reτ=130~2000 DNS ☆ log-law not given Lee et al[23] TCF Reτ=180~5186 DNS △ log-law not given Diaz-Daniel et al[24] TBL Reτ=409~625 DNS 
log-law 0.94~1.03 常用的摩阻测量方法可以分为直接测量法和间接测量法[25].摩阻天平是最典型的直接测量法[26], 采用浮动元件实现对摩阻的直接测量, 虽然操作简单, 但其测量精度受制造偏差以及安装误差等影响较大, 近年来随着机械加工技术的发展, 浮动元件传感器的尺寸可以加工至微米级, 这在一定程度上提高了测量的空间分辨率, 但其相对较小的测量体限制了进一步应用, 此外, 加工成本较高也是此测量技术的一个缺点.
对于间接测量法, 其基本原理是根据某些近壁物理量在剪切的作用下发生改变, 间接推导出摩阻.热传导法是比较常用的间接测量方法, 它的测量原理为根据壁面热流密度和表面摩阻的比拟关系间接测量摩阻, 热线[7, 19]、热膜[6]以及近些年来发展起来的微机电热学传感器(micro-electromechanical-systems, MEMS)[11, 27]均基于这种测量原理.这种方法的测量精度较高, 但随着Reynolds数增高, 测量不确定度会随着壁面热损失增大而逐渐变大[6].此外, 流场干扰一直是这些测量技术不可避免的问题.
Newton内摩擦定律也是常用的摩阻间接测量方法, 其测量原理为基于壁湍流黏性底层线性标度率的认识.前人研究表明[4], 在壁湍流靠近壁面y+≤5(上标+表示采用内尺度标度, y+=y/l*)的区域内速度与距离壁面的位置呈线性增加趋势: U+=y+(U+=U/uτ), 摩阻可以根据黏性底层的速度梯度来估算: τw=υρ∂U/∂y, 此方法因此也被称为速度梯度法, 速度梯度法的估算精度主要依赖于黏性底层中速度测量的精度.近年来, 粒子图像测速(particle image velocimetry, PIV)技术[17, 28-29]被越来越多地应用于流场的精细测量.作为一种光学测量方法, PIV技术能够避免流场干扰问题, 其基本原理为通过求解跨帧粒子图像对中查询窗口内(interrogation window, IW)示踪粒子的平均速度来近似代替流场速度, 空间分辨率为IW大小.常用的粒子图像处理方法为窗口互相关算法(window correlation, WC), IW为32 pixel×32 pixel, 此方法因空间分辨率较低不适用于求解速度梯度较大的场合.为了克服这一问题, Nguyen等[28]在TCF (Reτ=358)中采用长方形的IW(流向方向的尺寸大于法向方向尺寸)代替正方形IW求解瞬时速度场, 目的在于提高瞬时速度沿法向的空间分辨率, 他们所选用的IW为68 pixel×17 pixel. Willert[17]采用IW为256 pixel×1 pixel的互相关算法求解TBL(Reτ=240)近壁区瞬时速度场, 进一步根据近壁区瞬时速度梯度估算瞬时摩阻, 其统计结果与经验公式吻合较好, 见表 1. Zhu等[29]发展了joint-translation-shear-correlation(JTSC)算法, 其核心思想基于Nguyen等[28]的方法, 在互相关计算时同时考虑了速度以及速度梯度两个物理量, IW为256 pixel×32 pixel, 分别在低速以及高Mach数边界层中证实了此算法能够很好预估近壁区速度.
受Nguyen等[28]和Willert[17]工作启发, 本文开发了单行互相关算法(single row cross correlation, SRCC), 用于处理PIV粒子图像, 得到法向空间分辨率较高的瞬时速度场, 进而根据迭代拟合算法估算瞬时摩阻.此外, 还重点分析瞬时摩阻统计特性的Reynolds数效应以及多尺度结构特性.为了对比, 同时分析了相似Reynolds数范围内的DNS数据.本文第1节介绍了湍流边界层实验数据以及DNS数据来源; 第2节详细介绍了平均及瞬时摩阻估算方法; 第3节重点讨论了瞬时摩阻的基本统计特性, 包括前3阶统计矩、概率密度分布函数(probability density function, PDF)以及多尺度结构特性; 第4节给出了主要结论.
1. 实验数据及DNS数据介绍
本节将分别介绍平板湍流边界层的实验数据以及DNS数据来源.在下文中, x, y, z分别表示流向、法向和展向方向.
1.1 实验数据
本文的平板湍流边界层实验在北京航空航天大学低速回流式水洞中进行, 水洞实验段尺寸为18 m×1 m×1.2 m(长×宽×高), 水流通过安装在回流段尾部的动力系统驱动, 其流速可在0~1 000 mm/s范围内无级调节, 自由来流速度为U∞=500 mm/s时实验段的湍流度Tu约为0.8%, 结构示意图如图 1(a)所示.
将5块尺寸均为3 m×1 m(长×宽), 厚度为0.02 m的水力光滑的透明有机玻璃平板首尾连接起来组成一块总长度为15 m的平板, 并将其垂直于水洞实验段底壁放置, 用于产生湍流边界层.平板距离水洞内侧壁0.75 m, 由于本次实验的边界层最大厚度小于0.36 m, 所以侧壁边界层对平板湍流边界层影响可以忽略不计.实验拍摄的平面位置距离水洞底壁以及自由液面的距离均为0.5 cm, 能够最大限度地减小底壁边界层以及水面波的影响.为了保证充分发展的湍流, 在平板前缘下游0.4 m的位置粘贴上直径为3 mm的圆柱状拌线, PIV拍摄平面中心位置距离拌线12 m, 边界层实验示意图如图 1 (b)所示.通过调节电机转速, 本次实验共测量了5个流速的湍流边界层数据, 摩擦Reynolds数范围为Reτ=600~2 900, 按Reynolds数从低到高依次被标记为WT1~WT5.需指出的是, 由于使用的平板较长, 所以在测量位置处的边界层存在微弱的逆压梯度, 加速系数K(K=(ν/U∞2)dU∞/dx)约为0.4×10-7.前人研究表明较小的逆压梯度对近壁区的条带结构统计特性具有非常小的影响[30], 而低速条带与瞬时摩阻的动力学特性具有紧密关系[24], 因此推测本实验中的压力梯度对摩阻的统计特性不会产生显著影响, 而这一结论也将在之后的分析中得到证实.
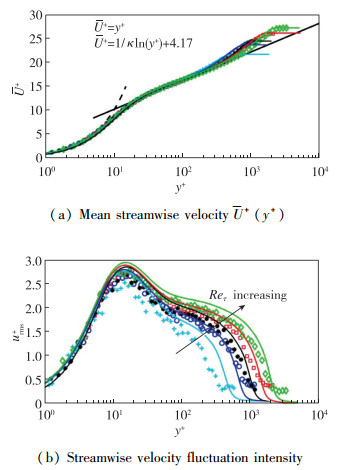
采用一维激光Doppler测速(1D laser Doppler velocimetry, 1D-LDV)技术测量了整个边界层范围内的流向速度, 内尺度无量纲的流向平均速度型U+(y+)和流向速度脉动强度urms+(y+)如图 2所示, 其中平均摩擦速度uτ为对流向平均速度型进行复合速度型拟合得到, 关于复合速度型经验公式的介绍可参考文献[31]. 图 2(a)中黑色虚线与实线分别表示线性率和对数率,其中Karman常数κ取为0.384, 可以看出, 不同测试工况的U+(y+)结果在线性区与对数区吻合较好.由于LDV测量体的窗口平均效应, urms+(y+)的强度略低于相似Reynolds数的DNS结果, 但在本文中LDV结果仅用于确定边界层参数, 并非用来估算摩阻, 所以无须进行误差补偿.边界层具体参数见表 2.
cases U∞/(mm/s) uτ/(mm/s) δ/mm δ*/mm θ/mm Reτ Reδ* Reθ symbols WT1 37.8 1.81 341 36.4 25.4 600 1340 930 
WT2 86.1 3.54 353 44.3 31.8 1 210 3 700 2 660 ○ WT3 147.9 5.90 257 32.3 23.4 1 510 4 760 3 450 
WT4 169.6 6.53 310 38.9 28.5 1970 6 420 4 700 
WT5 359.3 13.25 215 26.7 19.8 2840 9 560 7 070 
DNS1 — — — — — 610 1 420 990 
DNS2 — — — — — 870 2 540 1 800 
DNS3 — — — — — 1 300 3 970 2 860 
DNS4 — — — — — 1 880 6 410 4 650 
DNS5 — — — — — 2 540 8 870 6 500 
采用近壁PIV技术测量摩阻的实验示意图如图 1(b)所示.实验所用示踪粒子为直径10 μm, 密度1.05 g/cm3的空心玻璃微珠, 光源为功率8 W, 波长532 nm的连续激光器, 通过透镜组将激光片光厚度调整至1 mm并照亮x-y平面流场.采用单台高速CMOS(型号为Photron FastcamSA2/86K-M3, 分辨率为2 048 pixel×2 048 pixel)相机记录流场信息, 搭配镜头型号为TAMRON SP AF 180mm F/3.5 MACRO 1:1.视野范围(field of view, FOV)约为36.8×36.8 mm2, 对于测试的5个工况, 对应光学放大率约为0.03l*~0.22l*/pixel.采样频率f(Hz)根据相邻两张粒子图像的跨帧位移不超过12 pixel来确定, 具体数值可以参考表 3.由于CMOS高速相机存储空间有限(约为32 GB), 单次采样的最大样本数为5 456张, 为了保证统计结果的收敛性, 每个工况重复实验的次数均超过5次, 总的样本数N介于2×104~11×104, 无量纲采样时长为Tuτ/δ=1.16~6.72, TU∞/δ=24.2~182.1, 具体结果见表 3.
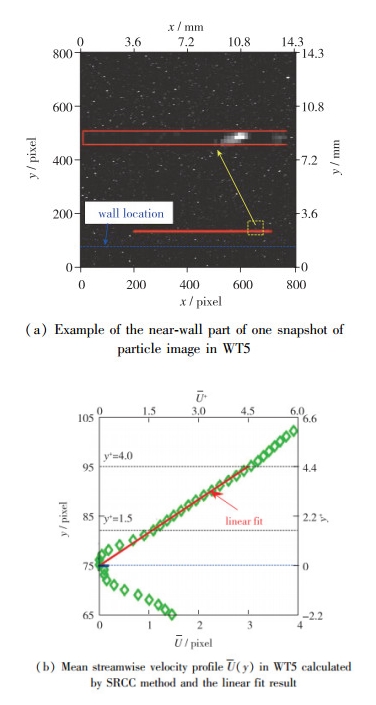
表 3 近壁PIV实验参数, SRCC算法空间分辨率以及近壁速度梯度估算不确定度表Table 3. Parameters of the PIV experiment, together with the spatial resolution and the estimated errors of the sublayer velocity gradient in SRCCcases f/Hz p.p.p N Tuτ/δ TU∞/δ Δx×Δy Δx+×Δy+ ε∂U/∂y WT1 125 0.005 8 27 280 1.16 24.2 512×2 17×0.06 0.07 WT2 250 0.004 3 49 104 1.97 47.9 512×2 35×0.14 0.18 WT3 500 0.004 7 70 928 3.26 81.7 512×2 51×0.20 0.62 WT4 500 0.002 5 92 752 3.91 101.4 512×4 62×0.48 0.17 WT5 1 000 0.003 2 109 120 6.72 182.1 512×4 110×0.86 1.41 近壁PIV实验需要解决的两个关键问题是壁面反光及粒子浓度.由于实验所用平板为光滑透明的有机玻璃板, 当激光片光垂直照射在壁面时, 能够最大限度允许光的透射, 有效抑制了壁面反光引起的光学污染, 这在图 3 (a)所示WT5工况中的粒子图像示例中可以清楚观察到, 从图中可以清楚地观察到壁面位置(蓝色虚线所示).因此, 不需要对粒子图像进行背景去除前处理[34].
对于粒子浓度低这一问题, Li等[18, 35]尝试在实验位置上游安装一个粒子喷射装置来补偿粒子浓度, 但是这种方法会由于射流效应对原始流场产生较大干扰, 所以本实验并没有采用类似的粒子浓度补偿方案. 表 3给出了近壁y+ < 30流层中的粒子浓度(particle per pixels, p.p.p.), 可以看出:本实验的p.p.p.略小于传统PIV实验数值[36], 为了提高互相关运算中相关峰的识别精度, 将SRCC算法的IW适当调大, 保证了每个IW中具有足够的灰度信息, 具体结果将在下文给出.
1.2 DNS数据
为了对比实验结果, 分析了相近Reynolds数范围的湍流边界层DNS数据, 数据来源于Jiménez组[3].按照Reynolds数从低到高, 5个工况分别记为DNS1~DNS5, 其中, 关于Reynolds数较低的两个工况(DNS1~DNS2)的介绍可以参考文献[32], 3个较高Reynolds数工况(DNS3~DNS5)可查阅文献[33].对于每个工况, 均下载了28个三维体式速度场, 其x-y平面范围为6δ×δ, 展向范围为6 000l*(DNS1~DNS2), 16 000l*(DNS3~DNS5).对于每个体式速度场, 沿展向等间距切割出96(DNS1~DNS2), 128(DNS3~DNS5)个瞬时速度切片, 速度场样本总数为2 688(DNS1~DNS2), 3 584(DNS3~DNS5). DNS数据的流向平均速度及流向速度脉动强度剖面见图 2.需要指出的是, 为了保证与实验结果的一致性, 同样采用了复合速度型公式对流向平均速度剖面进行拟合, Reynolds数结果见表 2.
2. 平均及瞬时摩阻估算方法
本文采用SRCC算法处理粒子图像.根据粒子浓度, WT1~WT3工况的IW为512 pixel×2 pixel, WT4~WT5工况IW选为512 pixel×4 pixel, 各工况的IW及其内尺度结果见表 3. 图 3(a)中红色实线框表示SRCC算法IW示意图,子图表示黄色方框的局部放大图,可以看出:由于本实验的空间放大率较高(约为11~18 μm/pixel), 示踪粒子在粒子图像中的平均直径大约为4~5 pixel, 大于传统PIV中的3 pixel.因此, 虽然粒子浓度略低, 但每个IW中大约包含了4~5个粒子, 其灰度信息足够进行互相关计算.需要指出的是, 由于SRCC算法IW的流向长度较大, 窗口平均效应会过滤掉瞬时速度场中特征长度小于IW的小尺度结构, 但对于大尺度结构影响较小.其对于瞬时摩阻统计及多尺度结构特性的影响有限, 关于误差分析可参考文献[37].
2.1 平均摩阻估算方法
图 3(b)给出了采用SRCC算法得到的WT5工况(p.p.p最低)的流向平均速度结果U+(y+).可以看出:在1.5≤y+≤4区间, 平均速度剖面具有明显的线性区, 在靠近壁面的位置, 粒子的黏附效应导致y+ < 1.5内的平均速度被低估.平均速度梯度可以通过对1.5≤y+≤4区间内的数据点进行最小二乘拟合得到.进一步根据Hutchins等[38], 平均速度梯度的估算不确定度ε∂U/∂y可通过下式估算
σˉU=√N∑i=1(ˉUi−ˆU)2−∂ˉU∂yN∑i=1(yi−ˆy)(ˉUi−ˆU)N−2 (1) σ∂ˉU/∂y=σˉU√N∑i=1(yi−ˆy)2 (2) ε∂ˉU/∂y=σ∂ˉU/∂y/∂ˉU∂y×100% (3) 式中, Ui和yi分别表示1.5≤y+≤4区间中第i个数据点(i=1, 2, …, N)的平均速度以及它所对应的法向高度, ˆU=N∑i=1ˉUi,ˆy=N∑i=1yi,σˉU表示实验数据点相对于线性拟合曲线的偏差, σ∂U/∂y表示速度梯度的估算偏差.如表 3所示, 所有实验工况的速度梯度不确定度均小于2%, 这一结果小于Hutchins等[38]采用热线测量的结果, 初步证实了SRCC算法估算平均速度梯度的可靠性.平均摩阻可根据ˉτw=vρ∂ˉU/∂y得到.
2.2 瞬时摩阻估算方法
图 4(a)给出了WT5工况某瞬时速度剖面示例, 从图中可以看出:黏性底层内的瞬时速度并不是典型的线性分布, 而是有些波动.因此, 不能对整个黏性底层内的瞬时速度进行线性拟合, 应该首先剔除掉不符合线性标度率的数据点, 然后再进行拟合得到瞬时速度梯度.为此, 发展了迭代拟合方法, 具体为:对于黏性底层y+≤5中的任意一个数据点, 对以此点为中心的邻域内5个数据点进行线性拟合, 如图 4(a)所示, 红、蓝色实线分别为红色数据点和蓝色数据点的线性拟合结果. 图 4 (b)给出了瞬时速度梯度不确定度ε∂U/∂y沿法向的变化趋势, ∂U/∂y可根据式(1)~(3)估算, 只须将式中平均速度U替换为瞬时速度U.可以看出: ε∂U/∂y在0.1%~30%之间波动, 其中, 靠近壁面的结果较大, 是由粒子的黏附效应导致(与图 3(b)结果一致).相较于平均速度, 瞬时速度梯度不确定度较大, 因此定义满足阈值条件ε∂U/∂y < 5%的数据点为符合线性标度率的点, ε∂U/∂y≥5%的点为坏点.通过多次迭代, 直到剔除掉所有不满足阈值条件的坏点, 再对剩余的数据点进行最小二乘拟合即可得到瞬时速度梯度以及瞬时摩阻.
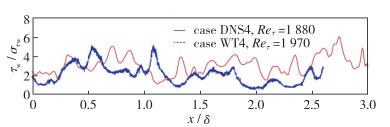
为了验证SRCC和迭代拟合方法估算瞬时摩阻的可靠性, 图 5对比了相近Reynolds数(Reτ≈1 800)实验(WT4)与DNS数据(DNS4)的瞬时摩阻空间信号τw(x), 其中实验结果为根据Taylor冻结假设从时序信号转化而来.根据Wang等[37], 瞬时摩阻的对流速度选择为uc+=12.从图中可以看出, 实验与DNS结果较为类似, 均呈现出多尺度脉动特性, 且波峰及波谷处的脉动幅值相当.此外, 由Q4事件主导的瞬时摩阻极值事件[39]均频繁地出现于实验及DNS结果中, 表明实验结果具有较高的精度.
3. 瞬时摩阻统计特性
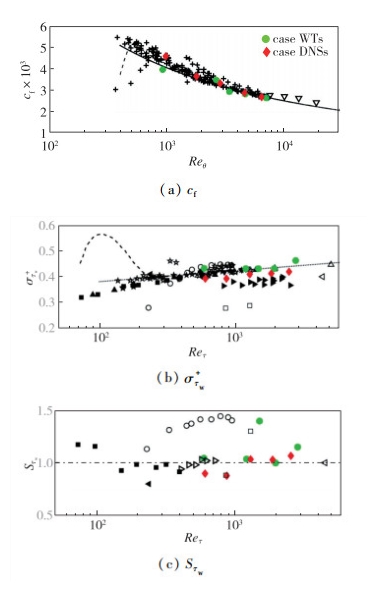
本节将重点分析瞬时摩阻的统计及多尺度结构特性, 包括前3阶统计矩, PDF曲线以及能谱分析结果. 图 6(a)给出了平均摩擦应力系数cf随着Reynolds数Reθ的变化趋势, 图中黑色实线为Nagib等[40]给出的经验公式cf=2(1/κlnReθ+4.127)-2, “+”表示Sillero等[33]的结果"▽"表表示Herpin等[41]的结果.可以看出本实验及DNS结果均与经验公式吻合较好, 其中实验测量误差在7%以内. 图 6(b)给出了采用平均摩阻无量纲的脉动强度στw+随着Reτ的变化趋势, 图中点线表示Schlatter等[13]给出的对数标度率στw+=0.298+0.018lnReτ, 虚线表示Diaz-Daniel等[24]的DNS结果.可以看出, 实验结果符合对数标度率, 其相对偏差在5%以内; DNS结果略小于经验值, 但其随Reynolds数增加仍然呈现对数增长规律, 相对误差在6%以内. 图 6(c)所示为摩阻的偏度Sτw随着Reτ的变化趋势, 可以看出偏度值约等于1, 但Reynolds数效应不明显.
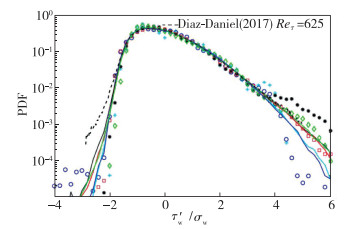
图 7给出了采用脉动强度无量纲的瞬时脉动摩阻信号的概率密度函数分布曲线PDF(τ′w/στw), 图中给出了Diaz-Daniel等[24]的最高Reynolds数(Reτ=625)结果, 可以看出不同Reynolds数结果在-2 < τ′w/στw < 3区间吻合较好, 没有明显的Reynolds数效应. Diaz-Daniel等[24] DNS研究表明在低Reynolds数下(Reτ=409~625)极值事件(τ′w/στw>3和τ′w/στw < -2)出现的概率随着Reynolds数增高而缓慢增加, 本文DNS1~DNS3(Reτ=600~1 300)工况结果表现出了类似现象, 但在更高Reynolds数下DNS3~DNS5, 极值事件出现的概率没有呈现明显的Reynolds数效应, 这与Sτw的弱Reynolds数效应相吻合.此外, 虽然Diaz-Daniel等[24]最高Reynolds数工况与DNS1工况Reτ较为接近, 但二者的PDF曲线在τ′w/στw>3和τ′w/στw < -2端仍然具有较大差异, 这可能是由于极值事件对于数值模拟的设置参数比较敏感, 比如转捩方式, 进出口条件等.
图 8给出了实验及DNS工况的瞬时摩阻一维预乘能谱曲线kxϕτ′wτ′w(λx), 其中特征波长λx分别采用内尺度l*, 混合尺度(l*δ)1/2以及外尺度δ标度, 纵坐标kxϕτ′wτ′w采用各自曲线的峰值(kxϕτ′wτ′w)max进行无量纲.为了对比, 重绘了Diaz-Daniel等[24]最高Reynolds数(Reτ=625)结果.可以看出, 相较于混合尺度及外尺度标度结果, 当λx采用内尺度无量纲时(见图 8(a)), 所有测试工况结果的重合度较好, 且与Diaz-Daniel等[24]的结果基本吻合, 这与Khoo等[7]在低Reynolds数TBL以及Gubian等[19]在低Reynolds数TCF的结论相一致.此外, 一维预乘能谱的峰值位置对应1 000l*, 近似等于近壁区低速条带的平均流向长度, 表明在当前中低Reynolds数范围内, 近壁区的低速条带结构主导着摩阻的动力学行为, 贡献了摩阻的主含能结构.
Örlü等[42]的DNS能谱分析结果表明: LSMs/VLSMs对于瞬时摩阻具有明显的印迹作用, 且其影响随Reynolds数升高而变大.然而Diaz-Daniel等[24]的一维预乘能谱曲线结果表明大尺度结构的能量并没有呈现明显的Reynolds数效应, 这与当前实验及DNS结果相一致, 表明在当前中低Reynolds数范围内, LSMs/VLSMs对于摩阻的印迹作用较小.可能的原因是对于外区非黏性的大尺度运动, 很难通过印迹作用影响到摩阻, 近壁区的黏性运动为摩阻提供了一层保护以阻止外区大尺度运动的影响, 外区LSMs/VLSMs主要通过调制作用对摩阻施加影响, 从而使得στw+~Reτ呈对数增长规律.
4. 结论
本文采用PIV技术测量了中低Reynolds数范围内(Reτ=600~2 900)光滑平板湍流边界层的瞬时摩阻, 同时分析了相似Reynolds数范围内的DNS数据.
采用SRCC算法处理PIV粒子图像可以得到法向空间分辨率较高(约为2~4 pixel)的瞬时速度场, 进一步采用迭代拟合技术估算瞬时摩阻.瞬时摩阻的前3阶统计矩与前人结果吻合较好, 采用平均摩阻无量纲的脉动强度遵循对数标度率στw+=0.298+0.018lnReτ, 证实了外区的大尺度结构对于摩阻具有影响.
瞬时摩阻的一维预乘能谱曲线遵循内尺度标度率, 峰值位置为1 000l*, 近似等于近壁区低速条带结构的平均长度, 表明低速条带结构主导着摩阻的动力学行为.此外, 大尺度结构的能量没有呈现随Reynolds数增高而增大的趋势, 表明外区大尺度结构对于摩阻的印迹作用较小, 这是由于外区非黏性的大尺度运动很难通过印迹作用渗入到壁面, 近壁区的黏性运动为摩阻提供了一层保护以阻止外区大尺度运动的影响.这一点可以从瞬时摩阻的偏度(Sτw≈1)以及PDF分布均呈现弱Reynolds数效应得到进一步证实.大尺度结构主要通过调制作用对摩阻的统计及多尺度结构特性施加影响.
-
表 1 前人对于瞬时摩阻统计特性研究结果总结(标记在图 6中应用)
Table 1 Summary of previous studies on the statistics of wall-shear stress (The symbols listed in the table are used in Fig. 6 for the related work)
references flow types Re methods symbols στw+ Sτw Alfredsson et al[6] TBL
TCFReδ=28 000
Reh=3 800,5 000flush-mounted hot wire/hot film none 0.4 1 Österlund [14] TBL Reθ=2 500~9 800 hot wire 
0.36~0.4 not given Miyagi et al[11] TCF Reh=8 758~17 517 micro shear stress imaging chip none 0.4 1 Keirsbulck et al[15] TCF Reτ=74~400 electrochemical probe ■ 0.32~0.40 0.91~1.17 Mathis et al[16] TBL Reτ=4 480 hot wire 
0.4 1 Willert[17] TBL Reτ=240 PIV 
0.41 0.80 Li et al[18] TBL Reθ=1 009~4 070 μ-PTV 
0.39~0.43 not given Gubian et al[19] TCF Reτ=230~950 flush-mounted hot wire ○ 0.28~0.44 1.13~1.44 Liu et al[20] TCF Reτ=860, 1 300 MPS □ 0.28/0.29 0.88/1.3 Abe et al[21] TCF Reτ=180, 395, 640 DNS ◇ log-law not given Hu et al[22] TCF Reτ=90~1 440 DNS ▲ log-law 0.96~1.14 Schlatter et al[13] TBL Reτ=130~2000 DNS ☆ log-law not given Lee et al[23] TCF Reτ=180~5186 DNS △ log-law not given Diaz-Daniel et al[24] TBL Reτ=409~625 DNS 
log-law 0.94~1.03 表 2 平板湍流边界层主要参数表(最后一栏标记应用在图 2,图 7和图 8中)
Table 2 Summary of the characteristic boundary layer parameters(The definition of the symbols is adopted in Fig. 2, Fig. 7 and Fig. 8)
cases U∞/(mm/s) uτ/(mm/s) δ/mm δ*/mm θ/mm Reτ Reδ* Reθ symbols WT1 37.8 1.81 341 36.4 25.4 600 1340 930 
WT2 86.1 3.54 353 44.3 31.8 1 210 3 700 2 660 ○ WT3 147.9 5.90 257 32.3 23.4 1 510 4 760 3 450 
WT4 169.6 6.53 310 38.9 28.5 1970 6 420 4 700 
WT5 359.3 13.25 215 26.7 19.8 2840 9 560 7 070 
DNS1 — — — — — 610 1 420 990 
DNS2 — — — — — 870 2 540 1 800 
DNS3 — — — — — 1 300 3 970 2 860 
DNS4 — — — — — 1 880 6 410 4 650 
DNS5 — — — — — 2 540 8 870 6 500 
表 3 近壁PIV实验参数, SRCC算法空间分辨率以及近壁速度梯度估算不确定度表
Table 3 Parameters of the PIV experiment, together with the spatial resolution and the estimated errors of the sublayer velocity gradient in SRCC
cases f/Hz p.p.p N Tuτ/δ TU∞/δ Δx×Δy Δx+×Δy+ ε∂U/∂y WT1 125 0.005 8 27 280 1.16 24.2 512×2 17×0.06 0.07 WT2 250 0.004 3 49 104 1.97 47.9 512×2 35×0.14 0.18 WT3 500 0.004 7 70 928 3.26 81.7 512×2 51×0.20 0.62 WT4 500 0.002 5 92 752 3.91 101.4 512×4 62×0.48 0.17 WT5 1 000 0.003 2 109 120 6.72 182.1 512×4 110×0.86 1.41 -
[1] Thibert J J, Reneaux J, Schmitt V. ONERA activities on drag reduction[C]. Proceedings of the 14th Congress of ICAS, Bonn: ICAS, 1990: 1053-1064.
[2] Dean B, Bhushan B. Shark-skin surfaces for fluid-drag reduction in turbulent flow:a review[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2010, 368(1929):4775-4806. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2010.0201
[3] Jiménez J. Coherent structures in wall-bounded turbu-lence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018, 842:1. DOI: 10.1017/jfm.2018.154
[4] Pope S B. Turbulent flows[M]. Britain: IOP Publis-hing, 2001.
[5] She Z S, Chen X, Hussain F. Universal Karman constant in canonical wall turbulence[C]. Proceedings of the 66th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of Fluid Dynamics. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: American Physical Society, 2013.
[6] Alfredsson P H, Johansson A V, Haritonidis J H, et al. The fluctuating wall-shear stress and the velocity field in the viscous sublayer[J]. The Physics of Fluids, 1988, 31(5):1026-1033. DOI: 10.1063/1.866783
[7] Khoo B C, Chew Y T, Teo C J. Near-wall hot-wire measurements. Part II:turbulence time scale, convective velocity and spectra in the viscous sublayer[J]. Experi-ments in Fluids, 2001, 31(5):494-505. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2001ExFl...31..494K
[8] Kunkel G J, Marusic I. An approximate amplitude attenuation correction for hot-film shear stress sensors[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2003, 34(2):285-290. DOI: 10.1007/s00348-002-0558-9
[9] Sheng J, Malkiel E, Katz J. Using digital holographic microscopy for simultaneous measurements of 3D near wall velocity and wall shear stress in a turbulent boundary layer[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2008, 45(6):1023-1035. DOI: 10.1007/s00348-008-0524-2
[10] Groβe S, Schröder W. High Reynolds number turbulent wind tunnel boundary layer wall-shear stress sensor[J]. Journal of Turbulence, 2009, 10:N14. DOI: 10.1080/14685240902953798
[11] Miyagi N, Kimura M, Shoji H, et al. Statistical analysis on wall shear stress of turbulent boundary layer in a channel flow using micro-shear stress imager[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2000, 21(5):576-581. DOI: 10.1016/S0142-727X(00)00047-3
[12] Obi S, Inoue K, Furukawa T, et al. Experimental study on the statistics of wall shear stress in turbulent channel flows[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 1996, 17(3):187-192. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0142727X96000410
[13] Schlatter P, Örlü R. Assessment of direct numerical simulation data of turbulent boundary layers[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2010, 659:116-126. DOI: 10.1017/S0022112010003113
[14] Österlund J M. Experimental studies of zero pressure-gradient turbulent boundary layer flow[D]. Stockholm, Sweden: Department of Mechanics, Royal Institute of Technology, 1999.
[15] Keirsbulck L, Labraga L, Gad-el-Hak M. Statistical properties of wall shear stress fluctuations in turbulent channel flows[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2012, 37:1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e24ce5fd1cce207bdbc0a657c8edafd1
[16] Mathis R, Marusic I, Chernyshenko S I, et al. Estimating wall-shear-stress fluctuations given an outer region input[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2013, 715:163-180. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10baf30c15cc5cdd956b299960c1a2b2
[17] Willert C E. High-speed particle image velocimetry for the efficient measurement of turbulence statistics[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2015, 56(1):17. DOI: 10.1007/s00348-014-1892-4
[18] Li W F, Roggenkamp D, Jessen W, et al. Reynolds number effects on the fluctuating velocity distribution in wall-bounded shear layers[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2017, 28(1):015302. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017MeScT..28a5302L
[19] Gubian P A, Stoker J, Medvescek J, et al. Evolution of wall shear stress with Reynolds number in fully developed turbulent channel flow experiments[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2019, 4(7):074606. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevFluids.4.074606
[20] Liu Y O, Klaas M, Schröder W. Measurements of the wall-shear stress distribution in turbulent channel flow using the micro-pillar shear stress sensor MPS3[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2019, 106:171-182. DOI: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2019.04.022
[21] Abe H, Kawamura H, Choi H. Very large-scale structures and their effects on the wall shear-stress fluctuations in a turbulent channel flow up to Reτ=640[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2004, 126(5):835-843. DOI: 10.1115/1.1789528
[22] Hu Z W, Morfey C L, Sandham N D. Wall pressure and shear stress spectra from direct simulations of channel flow[J]. AIAA Journal, 2006, 44(7):1541-1549. DOI: 10.2514/1.17638
[23] Lee M, Moser R D. Direct numerical simulation of turbulent channel flow up to Reτ≈5200[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2015, 774:395-415. http://journals.cambridge.org/abstract_S0022112015002682
[24] Diaz-Daniel C, Laizet S, Vassilicos J C. Wall shear stress fluctuations:mixed scaling and their effects on velocity fluctuations in a turbulent boundary layer[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2017, 29(5):055102.
[25] Winter K G. An outline of the techniques available for the measurement of skin friction in turbulent boundary layers[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 1979, 18:1-57. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0376042177900021
[26] 赵荣娟, 吕治国, 黄军, 等.基于压电敏感元件的摩阻天平设计[J].空气动力学学报, 2018, 36(4):555-560. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=KQDX201804002 Zhao R J, Lyu Z G, Huang J, et al. Design of skin friction balance based on piezoelectric ceramics[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2018, 36(4):555-560(in Chinese). http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=KQDX201804002
[27] Liu X H, Li Z Y, Wu C J, et al. Toward calibration-free wall shear stress measurement using a dual hot-film sensor and Kelvin bridges[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2018, 29(10):105303. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6501/aadb1b
[28] Nguyen C V, Wells J C. Direct measurement of fluid velocity gradients at a wall by PIV image processing with stereo reconstruction[J]. Journal of Visualization, 2006, 9(2):199-208. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=466fd4b9f8e150338e90de2a220a5c8d
[29] Zhu Y D, Jiang X Y, Zhang Y C, et al. Iterative PIV interrogation for complex wall-bounded flows[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2019, 30(9):095302. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=IOP_9531327
[30] Wang W K, Pan C, Wang J J. Wall-normal variation of Spanwise streak spacing in turbulent boundary layer with low-to-moderate Reynolds number[J]. Entropy, 2019, 21(1):24. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/330029129_Wall-Normal_Variation_of_Spanwise_Streak_Spacing_in_Turbulent_Boundary_Layer_With_Low-to-Moderate_Reynolds_Number
[31] Chauhan K A, Monkewitz P A, Nagib H M. Criteria for assessing experiments in zero pressure gradient boundary layers[J]. Fluid Dynamics Research, 2009, 41(2):328-332. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=874217a2819c46b706d585e9f5b7af46&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[32] Simens M P, Jiménez J, Hoyas S, et al. A high-resolution code for turbulent boundary layers[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2009, 228(11):4218-4231. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021999109001119
[33] Sillero J A, Jiménez J, Moser R D. One-point statistics for turbulent wall-bounded flows at Reynolds numbers up to δ+≈2000[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2013, 25(10):105102. DOI: 10.1063/1.4823831
[34] Mendez M A, Raiola M, Masullo A, et al. POD-based Background removal for particle image Velocimetry[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2017, 80:181-192. DOI: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.08.021
[35] Li W F, Wilhelm Jessen D R, Klass M, et al. Detection of rare back flow events in zero-pressure gradient turbu-lent boundary layers using micro-PTV/PIV[C]. Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Particle Image Velocimetry. Busan, Korea: The Korean Society Of Visualization, 2017.
[36] Okamoto K, Nishio S, Saga T, et al. Standard images for particle-image velocimetry[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2000, 11(6):685-691. DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/11/6/311
[37] Wang J J, Pan C, Wang J J. Characteristics of fluctuating wall-shear stress in a turbulent boundary layer at low-to-moderate Reynolds number[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2020, 5(7):074605. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevFluids.5.074605
[38] Hutchins N, Choi K S. Accurate measurements of local skin friction coefficient using hot-wire anemometry[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2002, 38(4/5):421-446. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b8dfd28bc325caa0f9a245e066e33ed2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[39] Pan C, Kwon Y. Extremely high wall-shear stress events in a turbulent boundary layer[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2018, 1001:012004. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/324491510_Extremely_high_wall-shear_stress_events_in_a_turbulent_boundary_layer
[40] Nagib H M, Chauhan K A, Monkewitz A. Approach to an asymptotic state for zero pressure gradient turbulent boundary layers[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A:Mathematical, Physical and Enginee-ring Sciences, 2007, 365(1852):755-770. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=887891ceaea68862a49944096902eff0
[41] Herpin S, Stanislas M, Foucaut J M, et al. Influence of the Reynolds number on the Vortical structures in the logarithmic region of turbulent boundary layers[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2013, 716:5-50. DOI: 10.1017/jfm.2012.491
[42] Örlü R, Schlatter P. On the fluctuating wall-shear stress in zero pressure-gradient turbulent boundary layer flows[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2011, 23(2):021704. DOI: 10.1063/1.3555191
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 陈怡纯,田海平,马国祯,陈纪仲. 湍流边界层均匀动量区统计分形特性的PIV实验研究. 力学学报. 2024(01): 34-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈纪仲,田海平,丁俊飞,马国祯,陈怡纯. 壁湍流摩阻时空信号无接触测量实验研究. 实验流体力学. 2024(04): 66-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张宇,唐湛棋,崔晓通,姜楠. 壁面局部动态扰动作用下湍流边界层多尺度相互作用. 气体物理. 2024(05): 19-29 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 许德辰,张悦,刘欣乐,李文丰. 基于粒子追踪测速的壁面摩擦应力测量. 实验流体力学. 2022(02): 131-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王少飞,潘翀,齐中阳. 基于卷积神经网络的近壁流动高分辨率平均速度场预测方法. 实验流体力学. 2022(03): 110-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 黄智康,刘锋,张欣羡,周毅. 可压缩平板边界层流动的湍流/非湍流界面层空间分布的统计特性. 南京理工大学学报. 2022(06): 709-718 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 翟少华,谢福兴,尹广洲,喜冠南. 间隙比对近壁不同钝体涡激振动特性的影响. 排灌机械工程学报. 2021(11): 1132-1138 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载:





 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS